Fda Bcs
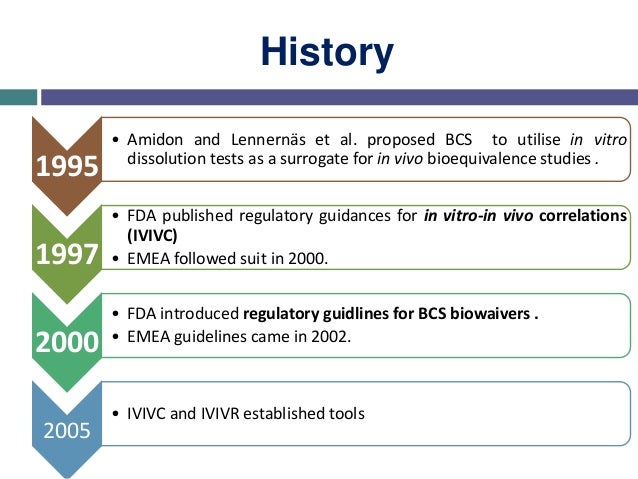
Fixed Dose Combinations Containing BCS Class 1, or Class 3, or Class 1 and 3. (BCS).4 This guidance includes biowaiver extension to BCS class 3 drug. The FDA issued a guidance for industry on waivers of in vivo bioavailability and bioequivalence studies for IR solid oral-dosage forms based on the BCS in August 2000 (5). The FDA’s Biopharmaceutics Classification System(BCS) 1 is based on the work of Amidon and coworkers 2 with the core idea being that in vitro methodology, centrally embracing permeability and solubility, with qualifications related to pH and dissolution, may qualify drug products for a waiver of in vivo bioequivalence studies.  The objective of the BCS is to predict in vivo performance of drug.
The objective of the BCS is to predict in vivo performance of drug.
Fda Bcs 1 Dissolution Guidance
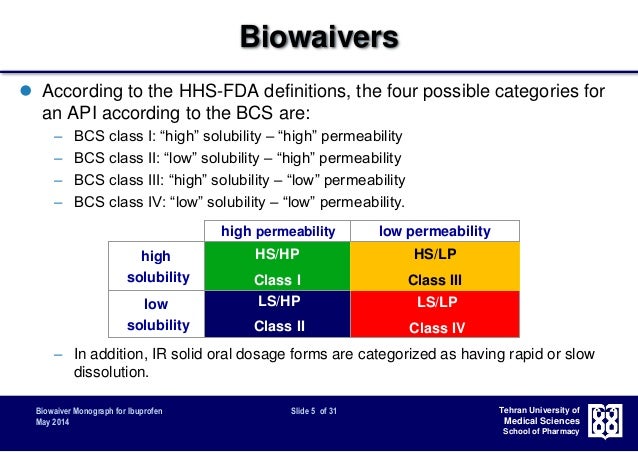
• • 1.5k Downloads • Abstract The Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS), based on aqueous solubility and intestinal permeability, has enjoyed wide use since 1995 as a mechanism for waiving in vivo bioavailability and bioequivalence studies. In 2000, the US-FDA was the first regulatory agency to publish guidance for industry describing how to meet criteria for requesting a waiver of in vivo bioavailability and bioequivalence studies for highly soluble, highly permeable (BCS Class I) drugs. Subsequently, the World Health Organization (WHO) and European Medicines Agency (EMA) published guidelines recommending how to obtain BCS biowaivers for BCS Class III drugs (high solubility, low permeability), in addition to Class I drugs. Tamil romantic mp3 songs free download. In 2015, the US-FDA became better harmonized with the EMA and WHO following publication of two guidances for industry outlining criteria for obtaining BCS biowaivers for both Class I and Class III drugs. A detailed review and comparison of the BCS Class I and Class III criteria currently recommended by the US-FDA, EMA, and WHO revealed good convergence of the three agencies with respect to BCS biowaiver criteria.